Socialization
In this lesson, you will learn how the self is connected to social phenomena, such as gender, race, and the media, and how interactions construct them all. You will be acquiring some new analytic tools, including the concepts of socialization and impression management. This lesson presents concepts of self from Freud, Mead, and Cooley; impression management and presentation of the self from Goffman; socialization; statuses and roles; and the social construction of emotions. You will be introduced to a new way of looking at the self—indeed, a new way of looking at your self—that emphasizes the role of the social in creating the individual. And you will be reminded of the reverse: as your society makes you who you are, you have a role (in fact, many roles) to play in shaping your society. The Case Study for this week allows you a chance to analzye how behaviors travel through social networks.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
Deadlines
Be sure to hand these in before the deadline
Read

Questions
If you have any questions at all about what you are supposed to do this week, please remember I am here to help. Reach out any time so we can support your success.
The least you need to know
Theoretical perspectives of the self


Socialization¶
In this lesson, you will learn how the self is connected to social phenomena, such as gender, race, and the media, and how interactions construct them all. You will be acquiring some new analytic tools, including the concepts of socialization and impression management. This lesson presents concepts of self from Freud, Mead, and Cooley; impression management and presentation of the self from Goffman; socialization; statuses and roles; and the social construction of emotions. You will be introduced to a new way of looking at the self—indeed, a new way of looking at your self—that emphasizes the role of the social in creating the individual. And you will be reminded of the reverse: as your society makes you who you are, you have a role (in fact, many roles) to play in shaping your society. The Case Study for this week allows you a chance to analzye how behaviors travel through social networks.
Learning Objectives¶
By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
Identify processes of socialization and theories of the self.
Compare socialization agents.
Analyze media content.
Deadlines¶
Be sure to hand these in before the deadline
InQuizitive Chapter 4 (Thursday at 9:30am)
Bechdel Test Application (Sunday at 10:00pm)
Read¶
‘Socialization’, Chapter 4 in Real World
Watch¶
Class Lecture recording. [Slides](https://www.dropbox.com/s/qsv057p6dcdf85a/05%20Socialization.pptx?dl=1ociological Perspectives)
Social Development
Socialization
Social Interaction & Performance
Questions¶
If you have any questions at all about what you are supposed to do this week, please remember I am here to help. Reach out any time so we can support your success.
Post it in the Slack #questions channel!
Signup for virtual office hours!
Email me or your TA.
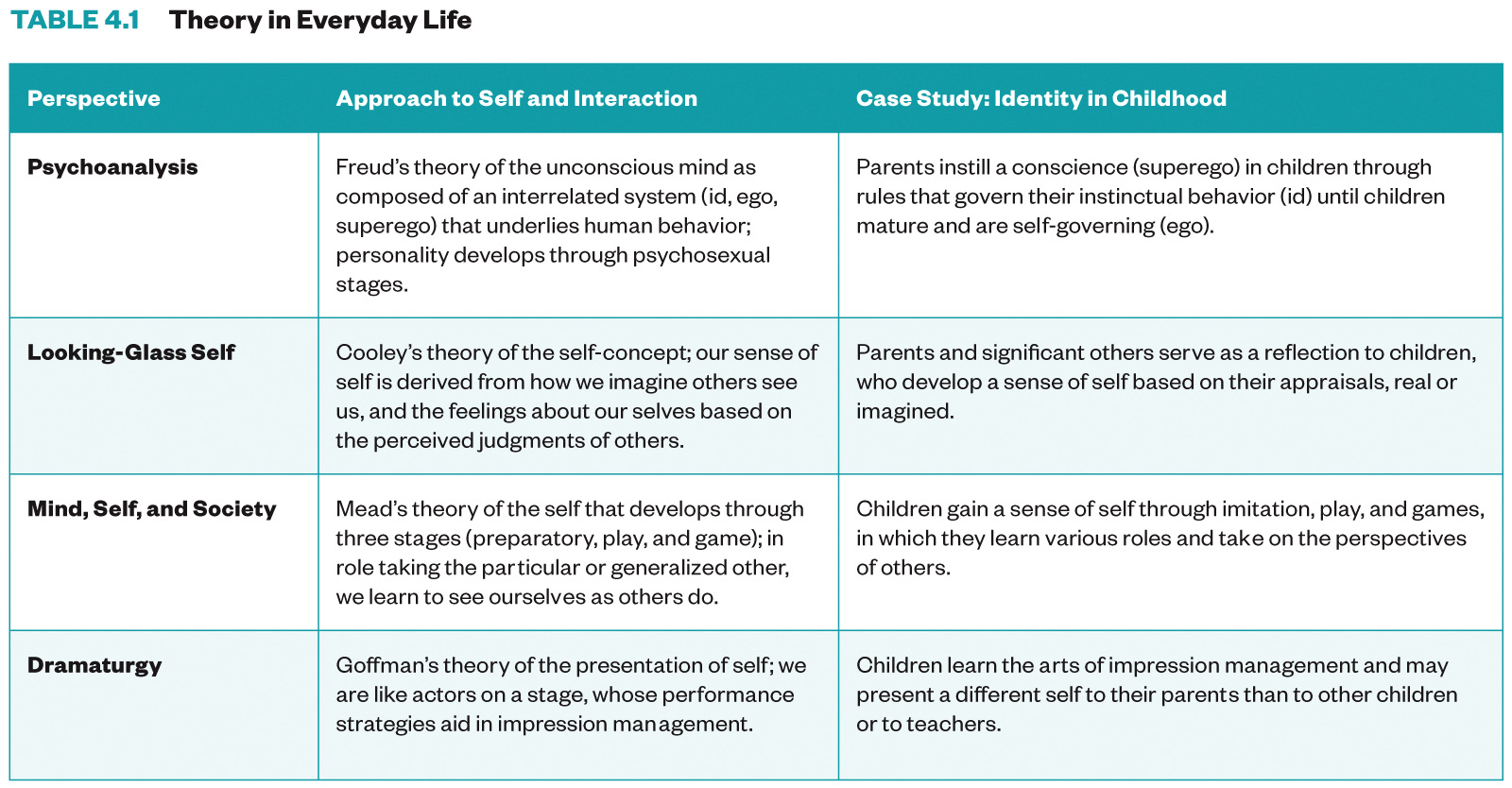
Lesson Keywords¶
Socialization
Self
Looking-glass self
Mead’s theory of the self
Generalized other
Thomas theorem
Definition of the situation
Dramaturgy
Impression management
Frontstage/backstage
Social construction
cooling the mark out
agents of socialization
hidden curriculum
total institutions
resocialization
status
ascribed status
embodied status
achieved status
master status
role
role conflict
role strain
emotional work/labor
agency
saturated self
civil inattention
The least you need to know¶
Theoretical perspectives of the self