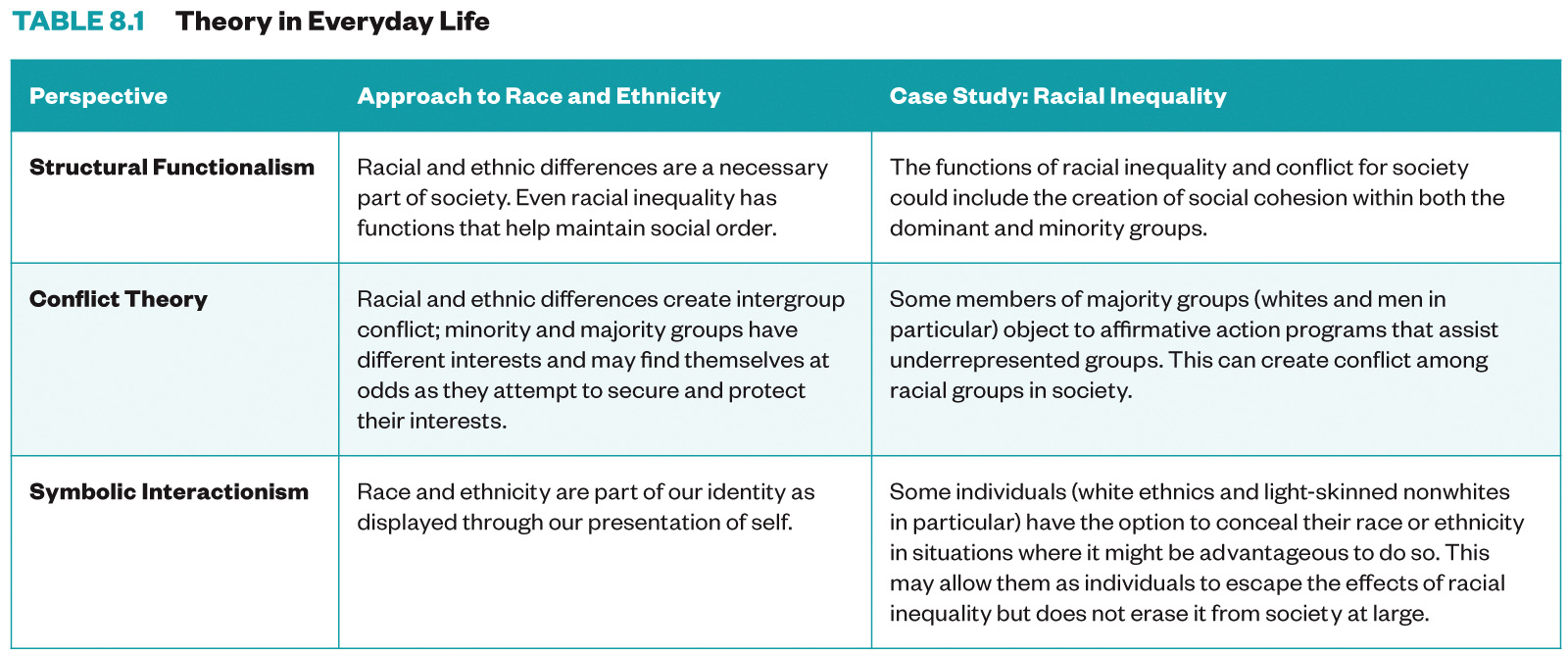
Race and Ethnicity¶
Central to the sociology is the understanding that race and ethnicity are socially constructed categories. While each is based on traits we may see as biological, such as skin color or facial features, the meanings attached to race and ethnicity are created, maintained, and modified over time through social processes in which we all take part. When a society categorizes people based on their race and ethnicity (and all do), it creates a system of stratification that leads to inequality. Society’s resources—wealth, power, privilege, opportunity—are distributed according to these categories, thereby perpetuating inequalities that are all too familiar here in the United States. In this lesson, you will also come to understand the importance of race and ethnicity in forming individual identity. Our racial and ethnic identities have profound effects on our sense of self, and our bonds to other people may be based on shared identities—or may transcend those categories entirely.
Learning Objectives¶
By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
Understand central concepts in the sociology of race and ethnicity and how major sociological perspectives view race and ethnicity.
Describe the impact of racism on life chances.
Deadlines¶
Be sure to hand these in before the deadline
InQuizitive Chapter Set 8 (Thursday at 9:30am)
Racial Dot Map application (Sunday at 10:00pm)
Banished reflection (Sunday at 10:00pm)
Discuss (Thursday during class):¶
Coded Bias¶

We will use the documentary film Coded Bias as an opportunity to explore the sociology of race and ethnicity. We will watch it together during class.
Be sure to have the movie ready to go at the start of class.
Login to the course Slack by 9:45am and say hi to your group!
Questions¶
If you have any questions at all about what you are supposed to do on this lesson, please remember I am here to help. Reach out any time so I can support your success.
Post it in the Slack #questions channel!
Signup for virtual office hours!
Email me or your TA.
Lesson Keywords¶
race
ethnicity
symbolic & situational ethnicity
minority group
racism
prejudice
discrimination
individual and institutional discrimination
white nationalism
privilege
color-blind racism
race consciousness
microaggressions
Reverse racism
antiracist allies
Critical race theory
passing
double-consciousness
embodied identity
Intersectionality
Race, Ethnicity, and Life
Chancesracial and cultural assimilation